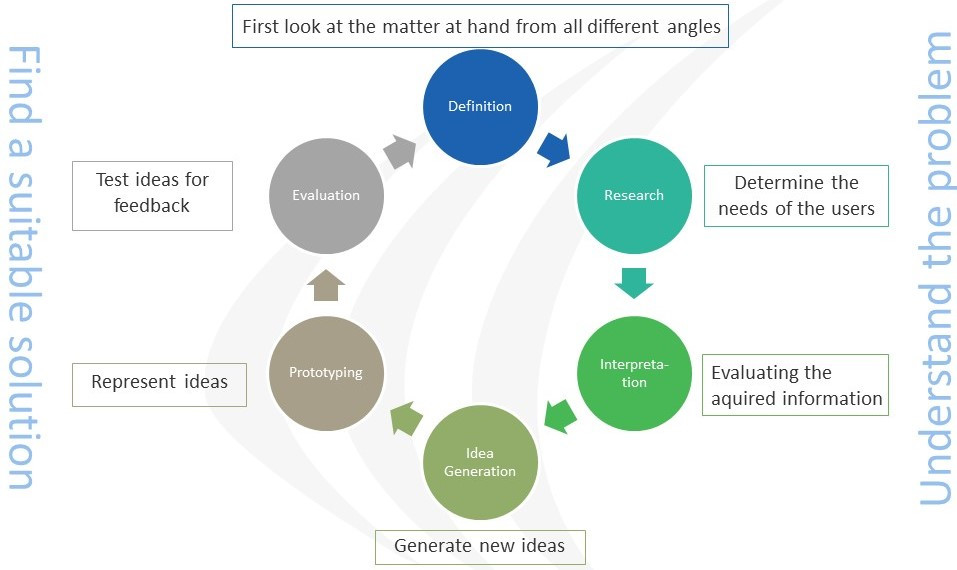
Design Thinking is a systematic, human-centered approach to solving complex problems within all aspects of life. These are the six process steps.
Definition: First look at the matter at hand from all different angles
generally the starting point
Ask questions
learn about the audience for whom you are designing
collect examples of other attempts to solve the same issue identify existing obstacles
Research: Determine the needs of the users
identify the needs and motivations of end-users
What is the team going to research?
Conducting interviews
Gaining a deeper understanding of the problem and the users
Interpretation: Evaluating the aquired information
Evaluate the acquired information
Create an overview of the insights
Cluster the information
Recognize certain needs relating to a group of users
Clear vision of the users, their needs, fears, and goals is established
Idea Generation: Generate new ideas
generate as many ideas as possible to serve these identified needs
log your brainstorming session
do not judge or debate ideas as this limits creativity
Prototyping: Represent ideas
build a representation of one or more of your ideas to show others
combine, expand, and refine ideas
create multiple drafts
Evaluation: Test ideas for feedback
seek feedback from a diverse group of people including end-users
review the objective and determine if the solution met its goals
avoid consensus thinking and ownership of ideas
discuss what could be improved