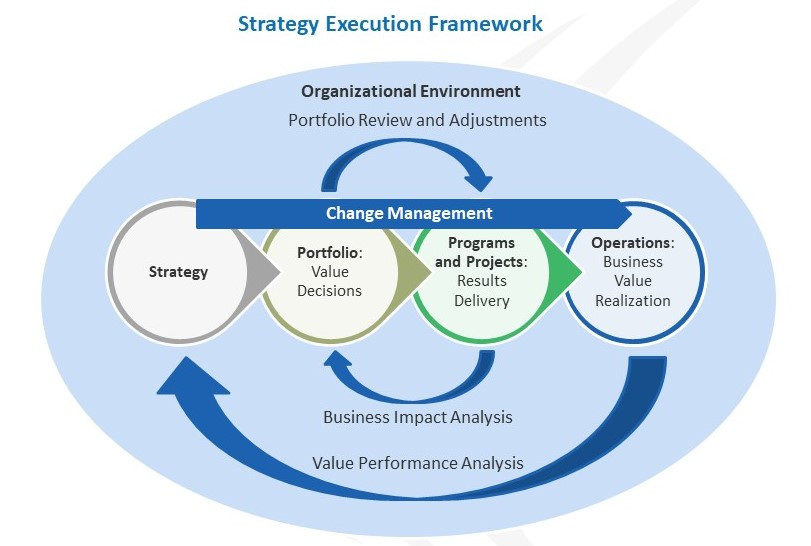
Building a competitive advantage with the strategy execution framework of OPM are embedded with change management.
Key factors for the strategy execution framework of OPM address critical success factors, potential barriers, lack of synergy, and the capabilities of a sponsor function in the organization.
Today’s continually evolving business environment requires constant change for organizations to stay competitive. The strategy translates the vision developed at the execution into changes that will produce tangible benefits and deliver value to stakeholders, ensuring continued growth and competitive advantage. These changes can be revolutionary such as a merger, acquisition, or business transformation, or evolutionary such as delivering new capabilities or services to the organization.
Organizational strategy is an input into the OPM strategy execution framework. It is based on the organization’s mission, vision, and values. This strategy acts as a roadmap for the remaining framework elements.
Portfolio management is used to determine which initiatives the organization should undertake in order to fulfill its strategy. It aligns the work and resources.
Program and project management is used to deliver the initiatives of the organization. Strategy alignment continues and the achievement is apparent when the results of the initiative are transitioned to the operations.
The OPM strategy execution framework includes multiple analysis and feedback loops. Business impact analysis collects results data from programs and projects and feeds it back into the portfolio. The impact on the business is then determined. This assessment is completed at the end of projects, but also at regular intervals.
The portfolio review and adjustment loop is meant to align and realign to the strategy. The portfolio analyzes current market trends and adjusts the portfolio of initiatives to reflect these changing conditions.
Outcomes of the programs and projects are transitioned into operations of the business where the business value can be measured.
This final feedback loop provides the business with value realization data delivered from initiatives to the business. It is an input for future strategy development and a measure for the benefits.
This represents the policies and practices of the organization. These are called organizational enablers and include the organizational competencies required to deliver strategy. This is where the integration of the OPM strategy execution framework and change management occur.
Creating a strategy execution framework is not a one-time activity. In order to fulfill the vision of the organization, it needs to mature and evolve. Continuous process improvement should be part of the values of the organization and be applied to the framework.
The context of an organization represents the environments in which an organization is situated and how it structures itself to respond to these environments. The primary environment is the industry in which the organization operates and the other include the size and structure of the organization as well as its geographic distribution.
To summarize, the OPM is a business approach for the deployment and delivery of organizational strategy through the implementation of portfolio, program, and project management. IT is an adaptive approach for fitting the capabilities to the unique context of the organization. Process improvement principles may be applied to all of the disciplines of OPM to achieve the benefits.